DDS 560/C Dynamic Dilution System
Dynamic Dilution System DDS 560/C for variable-adjustable dilution of aerosols at variable air flow rates
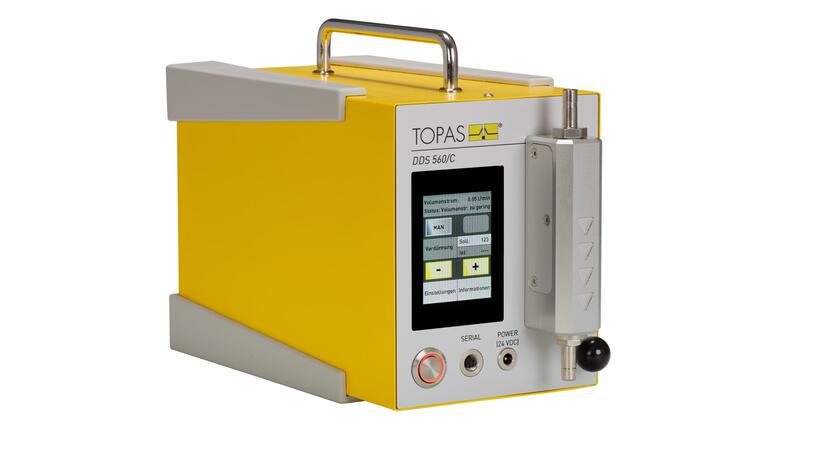
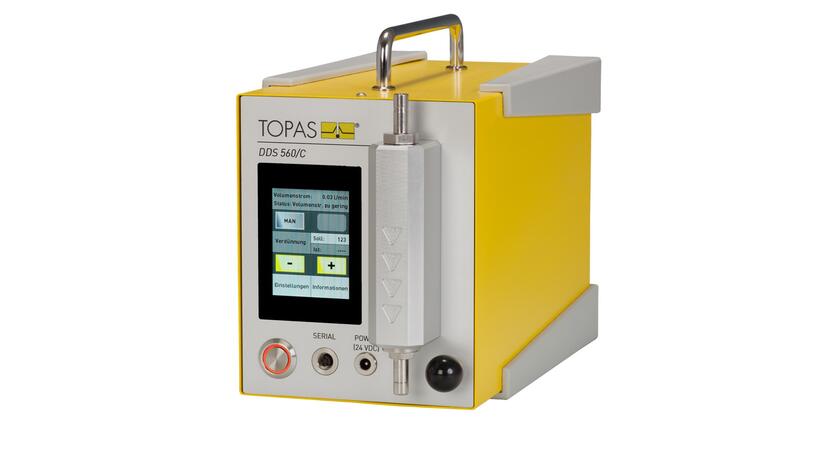
The DDS 560/C is an aerosol conditioning system that serves for free-adjustable and defined reduction of the particle number concentrations. Moreover, the dilution system can be passively operated by various aerosol sample flow rates.
Aerosol conditioning by dilution is one basic measure for analyses of aerosols. For example, numerous aerosol-analytical instruments are limited to specific concentration levels. Too high concentrations can cause a false estimate of aerosol characteristics due to the re-entrainment of deposited particles, coincidence effects within optical particle counters or insufficient bipolar neutralisation during differential mobility analyses.
Standards
VDI 3491-6
VDI 3491-15
download
product sheet DDS 560/CBenefits
- free adjustable dilution factor over wide range (approx. one decade)
- compatible with various aerosol-analytical instruments (i.e., variable flow rate)
- automatic readjustment of setting value of dilution
- stand-alone or remote-controlled operation with parameter monitoring
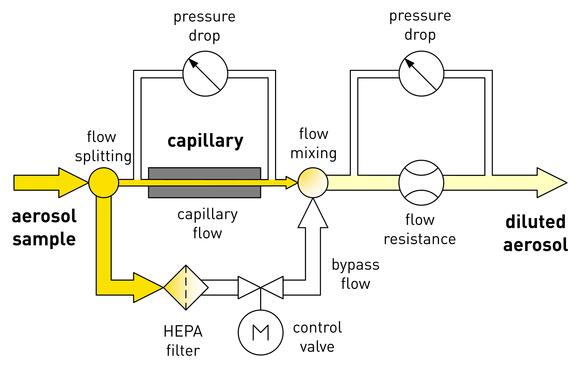
The DDS 560/C principal of operation is based on a splitting of the aerosol sample flow rate into a bypass and a capillary flow rate. All particles within the bypass flow rate are removed by a HEPA filter. The capillary flow is substantially lower than the bypass flow. Both the capillary flow rate and the total flow rate are determined via pressure drop measurement.
The control valve in the bypass flow rate path serves for adjusting the bypass flow rate and therefore the dilution ratio. After the capillary, all flow rates are merged.
| Parameter title | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| setting parameter | - | dilution factor |
| setting range (depending on flow rate) | - | 5 ... 200 (@ 0,5 L/min); 10 ... 370 (@ 1,0 L/min); 30 ... 190 (@ 3,0 L/min) |
| setting resolution | - | stepwise by 1 or 10 |
| volumetric flow rate, inlet | L/min | 0,5 ... 3,0 (continously variable) |
| power supply | - | 24 V DC (power adapter) |
| operating medium | - | air (others on request) |
| communication interface | - | RS232 (M9 IP67, 5 pole) |
| user interface | - | touch screen |
| set up time | s | max. 10 |
| power consumption | W | max. 25 |
| noise emission | dB(A) | not relevant |
| hose connector | mm | Ø 8 (outer diameter) |
| dimensions (w × h × d) | mm | 140 × 285 × 200 |
| weight | kg | 3,3 |
- antistatic hose (7,9 mm)
- HEPA fitler
-
Göhler D., Aslanyan L., Oelschlägel K., Bucur P., Buggisch J., Azhari N., Rudolph A., Roger S., Stintz M., Bausch D., Demtröder C., Ouaissi M. and Giger-Pabst U. Performance of intraoperative surgical smoke management technologies for laparoscopic surgery: A comparative in-vivo pig study J. Aerosol Sci. 177 (2024) 0, 106309
dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2023.106309 -
Tran S., Iida K., Yashiro K., Murashima Y., Sakurai H. and Olfert J. S. Determining the cutoff diameter and counting efficiency of optical particle counters with an aerodynamic aerosol classifier and an inkjet aerosol generator Aerosol Sci. Technol. 54 (2020) 11, 1335 - 1344
dx.doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2020.1777252 -
Kretzschmar, B.S.M.; Bergelt, P.; Göhler, D.; Firmbach, F.; Köcher, R.; Heft, A.; Stintz, M. & Grünler, B. Modulation of silica layer properties by varying the granulometric state of tetraethyl orthosilicate precursor aerosols during combustion chemical vapour deposition (CCVD) Aerosol Sci. Technol. 54 (2020) 10, 1124 - 1134
dx.doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2020.1762845 -
Göhler D., Stintz M. Granulometric characterization of airborne particulate release during spray application of nanoparticle-doped coatings. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 16 (2014) 2520,
dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2520-1 -
Mittmann-Frank M., Berger H., Rupf S., Wennemuth G., Pospiech P., Hannig M. and Buchter A. Exposition gegenüber Nanopartikeln und neuen Materialien in der Zahnheilkunde Zentralblatt für Arbeitsmedizin, Arbeitsschutz und Ergonomie 61 (2011) 0, 40-53
dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03344980